Finned tube radiators (referred to as radiators, also known as heat dissipation pipes, air heaters, and air heat exchangers): use refrigerants to cool air, or use heat media to heat air, or use cold water to recover air waste heat, etc.
Warm water, steam or high temperature heat transfer oil can heat the air, and pass through brine or low temperature water to cool the air.
Finned tube radiators can be widely used in light industry, construction, machinery, textile, printing and dyeing, electronics, food, starch, medicine, metallurgy, coating and other industries for hot air heating, air conditioning, cooling, condensation, dehumidification, drying wait.
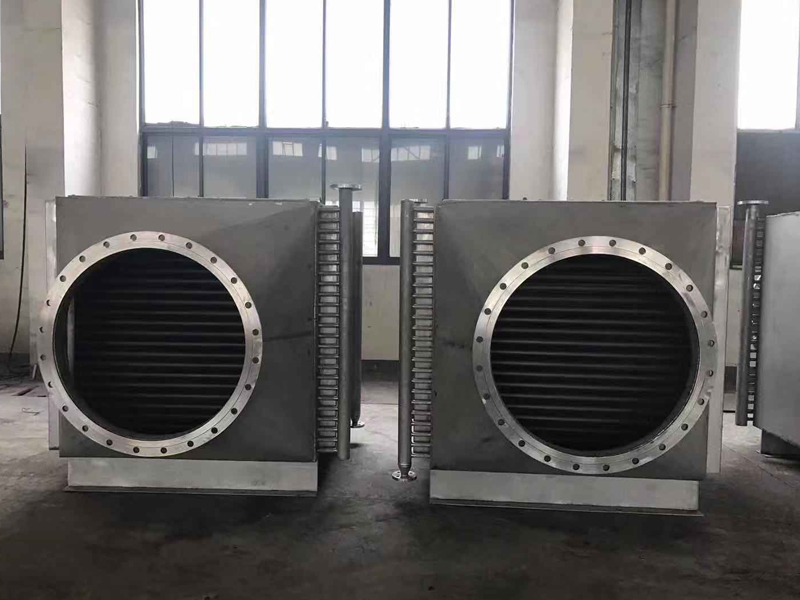

Heating Radiator: It is one of the applications of radiators, including heaters and radiators.
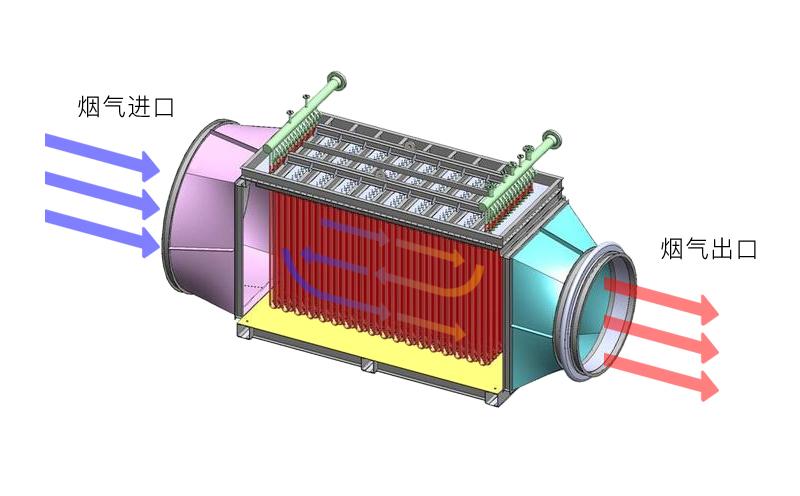
Finned tube radiator structure: heat dissipation pipe, inlet and outlet main pipe, frame.
Wherein, the heat dissipation pipe is composed of heat dissipation tube bundles, and the heat dissipation pipe is composed of base pipes and fins.
The quality of the heat pipe determines the heat exchange effect, the arrangement of the heat pipe affects the air resistance, and the installation method of the heat pipe determines the ability to withstand the temperature difference (thermal expansion and cold contraction).
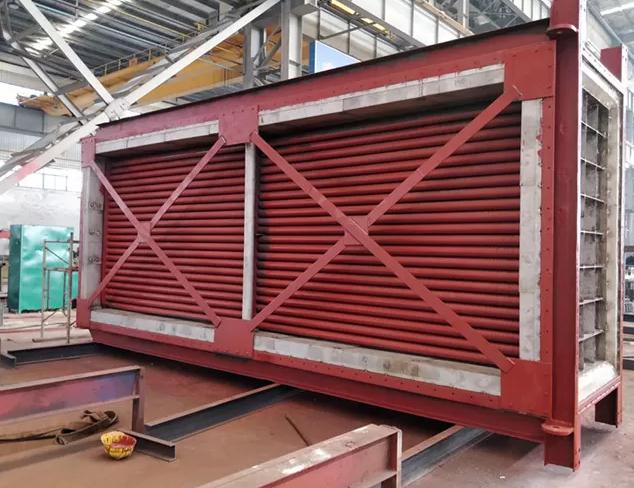

Commonly used finned tube radiator installation methods: frame fixed type (SRZ type, SRL type, S type), frame support type (GL type, U type).
Among them, the frame fixed type, the heat dissipation pipe is directly welded to the frame box, the structure is simple, and is generally used for heat medium or refrigerant below 180 °C; the frame support type, the heat dissipation pipe passes through the perforated plate of the frame, and is welded with the connecting pipe (or elbow) , generally used above 180°C
Get on the heat medium.
Commonly used finned tube cooling tube types: steel cooling tubes (steel tubes wrapped around steel fins, high-frequency welded tubes), steel-aluminum composite cooling tubes (steel tubes rolled aluminum fins), copper cooling tubes (copper tubes wrapped around copper fins, copper Tube sleeve aluminum sheet, copper tube sleeve copper sheet), copper-aluminum composite heat pipe (tube rolled aluminum fin), stainless steel heat pipe (stainless steel tube around stainless steel fin, high-frequency welded pipe).
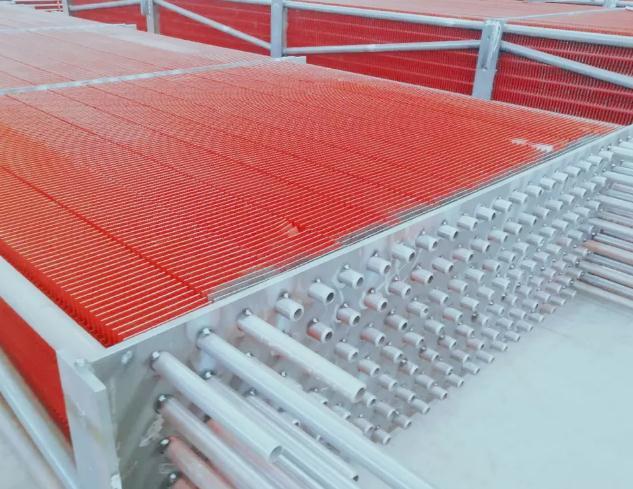

The main technical parameters of the finned tube radiator: cooling area, ventilation net cross-sectional area, heat transfer coefficient.
Among them, the heat dissipation area affects the heat dissipation, which is also the main cost parameter of the radiator; the ventilation net cross-sectional area affects the ventilation resistance; the heat transfer coefficient affects the heat transfer effect.
Finned tube radiator selection parameters: heat medium (steam, hot water), hot air, materials, heat transfer oil, and solutions of other media.
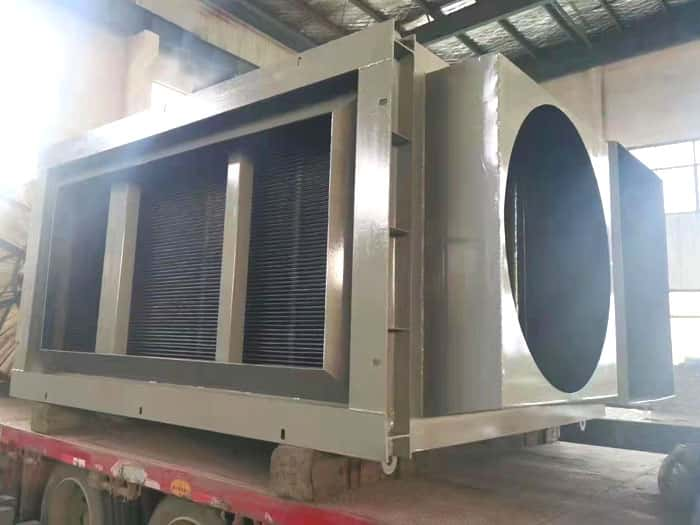

Among them: steam (pressure, temperature), hot water (water inlet temperature, outlet water temperature, flow rate), hot air (flow rate, inlet air temperature, humidity (water content), outlet air temperature, air resistance), material (heat consumption, evaporation water), heat transfer oil (inlet temperature, flow).
Selection parameters of heat preservation finned tube radiator: heat medium (steam, hot water), space, region, heat preservation.
Among them: steam (pressure, temperature), hot water (inlet water temperature, outlet water temperature, flow rate), space (length, width, height).
